Introduction
Physical Therapy in Venice for Foot
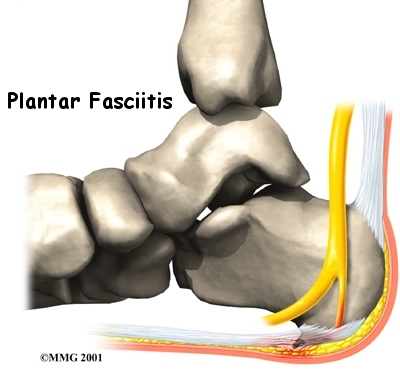
Welcome to FYZICAL Venice's patient resource about Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain).
Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis is the correct term to use when there is active inflammation. Plantar fasciosis is more accurate when there is no inflammation but chronic degeneration instead. Acute plantar fasciitis is defined as inflammation of the origin of the plantar fascia and fascial structures around the area. Plantar fasciitis or fasciosis is usually just on one side. In about 30 per cent of all cases, both feet are affected.
This article will help you understand:
- how plantar fasciitis develops
- how the condition causes problems
- what can be done for your pain
Anatomy
Where is the plantar fascia, and what does it do?
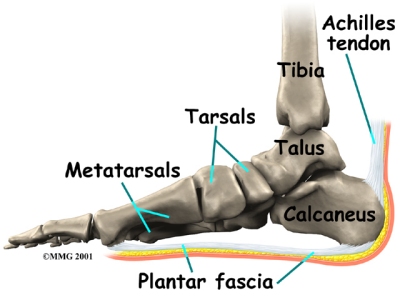 The plantar fascia (also known as the plantar aponeurosis) is a thick band of connective tissue. It runs from the front of the heel bone (calcaneus) to the ball of the foot. This dense strip of tissue helps support the arch of the foot by acting something like the string on an archer's bow. It is the source of the painful condition plantar fasciitis.
The plantar fascia (also known as the plantar aponeurosis) is a thick band of connective tissue. It runs from the front of the heel bone (calcaneus) to the ball of the foot. This dense strip of tissue helps support the arch of the foot by acting something like the string on an archer's bow. It is the source of the painful condition plantar fasciitis.
The plantar fascia is made up of collagen fibers oriented in a lengthwise direction from toes to heel (or heel to toes). There are three separate parts: the medial component (closest to the big toe), the central component, and the lateral component (on the little toe side). The central portion is the largest and most prominent.
Both the plantar fascia and the Achilles' tendon attach to the calcaneus. The connections are separate in the adult foot. Although they function separately, there is an indirect relationship. If the toes are pulled back toward the face, the plantar fascia tightens up. This position is very painful for someone with plantar fasciitis. Force generated in the Achilles’ tendon increases the strain on the plantar fascia. This is called the windlass mechanism. Later, we’ll discuss how this mechanism is used to treat plantar fasciitis with stretching and night splints.
Related Document: FYZICAL Venice's Guide to Foot Anatomy
Causes
How does plantar fasciitis develop?
Plantar fasciitis can come from a number of underlying causes. Finding the precise reason for the heel pain is sometimes difficult.
 As you can imagine, when the foot is on the ground a tremendous amount of force (the full weight of the body) is concentrated on the plantar fascia. This force stretches the plantar fascia as the arch of the foot tries to flatten from the weight of your body. This is just how the string on a bow is stretched by the force of the bow trying to straighten. This leads to stress on the plantar fascia where it attaches to the heel bone. Small tears of the fascia can result. These tears are normally repaired by the body.
As you can imagine, when the foot is on the ground a tremendous amount of force (the full weight of the body) is concentrated on the plantar fascia. This force stretches the plantar fascia as the arch of the foot tries to flatten from the weight of your body. This is just how the string on a bow is stretched by the force of the bow trying to straighten. This leads to stress on the plantar fascia where it attaches to the heel bone. Small tears of the fascia can result. These tears are normally repaired by the body.
As this process of injury and repair repeats itself over and over again, bone spur (a pointed outgrowth of the bone) sometimes forms as the body's response to try to firmly attach the fascia to the heelbone. This appears on an X-ray of the foot as a heel spur. Bone spurs occur along with plantar fasciitis but they are not the cause of the problem.
As we age, the very important fat pad that makes up the fleshy portion of the heel becomes thinner and degenerates (starts to break down). This can lead to inadequate padding on the heel. With less of a protective pad on the heel, there is a reduced amount of shock absorption. These are additional factors that might lead to plantar fasciitis.
Fat Pad
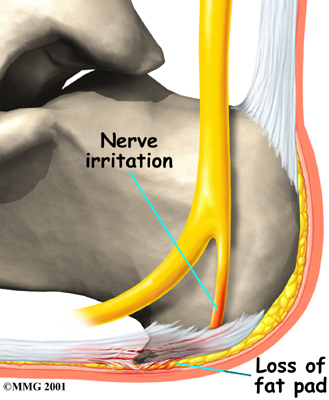
Some physicians feel that the small nerves that travel under the plantar fascia on their way to the forefoot become irritated and may contribute to the pain. But some studies have been able to show that pain from compression of the nerve is different from plantar fasciitis pain. In many cases, the actual source of the painful heel may not be defined clearly.
Symptoms
What does plantar fasciitis feel like?
The symptoms of plantar fasciitis include pain along the inside edge of the heel near the arch of the foot. The pain is worse when weight is placed on the foot. This is usually most pronounced in the morning when the foot is first placed on the floor.
Prolonged standing can also increase the painful symptoms. It may feel better after activity but most patients report increased pain by the end of the day. Pressing on this part of the heel causes tenderness. Pulling the toes back toward the face can be very painful.
Diagnosis
How do health care providers diagnose the condition?
When you first visit FYZICAL Venice, our Physical Therapist will examine your foot and speak with you about the history of your problem. Diagnosis of plantar fasciitis is generally made during the history and physical examination. There are several conditions that can cause heel pain, and plantar fasciitis must be distinguished from these conditions.
Some patients may be referred to a doctor for further diagnosis. Once your diagnostic examination is complete, the Physical Therapists at FYZICAL Venice have treatment options that will help speed your recovery, so that you can more quickly return to your active lifestyle.
Our Treatment
Non-surgical Rehabilitation
Nonsurgical management of plantar fasciitis is successful in 90 per cent of all cases. When you begin therapy at FYZICAL Venice, our Physical Therapist will design exercises to improve flexibility in the calf muscles, Achilles' tendon, and the plantar fascia.
We will apply treatments to the painful area to help control pain and swelling. Examples include ultrasound, ice packs, and soft-tissue massage. Our Physical Therapy sessions sometimes include iontophoresis, which uses a mild electrical current to push anti-inflammatory medicine, prescribed by your doctor, into the sore area.
We may have a customized arch support, or orthotic, designed to support the arch of your foot and to help cushion your heel. Supporting the arch with a well fitted orthotic may help reduce pressure on the plantar fascia. Alternatively, we may recommend placing a special type of insert into the shoe, called a heel cup. This device can also reduce the pressure on the sore area. Wearing a silicone heel pad adds cushion to a heel that has lost some of the fat pad through degeneration.
Your Physical Therapist will also provide ideas for therapies that you can perform at home, such as doing your stretches for the calf muscles and the plantar fascia. We may also have you fit with a night splint to wear while you sleep. The night splint keeps your foot from bending downward and places a mild stretch on the calf muscles and the plantar fascia. Some people seem to get better faster when using a night splint and report having less heel pain when placing the sore foot on the ground in the morning.
We find that many times it takes a combination of different approaches to get the best results for patients with plantar fasciitis. There isn’t a one-size-fits-all plan. Some patients do best with a combination of heel padding, medications, and stretching. If this doesn’t provide relief from symptoms within four to six weeks, then we may advise additional Physical Therapy and orthotics.
Finding the right combination for you may take some time. Don't be discouraged if it takes a few weeks to a few months to find the right fit for you. Most of the time, the condition is self-limiting. This means it doesn't last forever but does get better with a little time and attention. But in some cases, it can take up to a full year or more for the problem to be resolved.
Post-surgical Rehabilitation
Although recovery rates vary among patients, it generally takes several weeks before the tissues are well healed after surgery. The incision is protected with a bandage or dressing for about one week after surgery. You will probably use crutches briefly, and your Physical Therapist can help you learn to properly use your crutches to avoid placing weight of your foot while it heals.
The stitches are generally removed in 10 to 14 days. However, if your surgeon used sutures that dissolve, you won't need to have the stitches taken out. You should be released to full activity in about six weeks.
Surgical release of the plantar fascia decreases stiffness in the arch. However, it can also lead to collapse of the longitudinal (lengthwise) arch of the foot. Releasing the fascia alters the biomechanics of the foot and may decrease stability of the foot arch. The result may be increased stress on the other plantar ligaments and bones. Fractures and instability have been reported in up to 40 per cent of patients who have a plantar fasciotomy.
Throughout your post-surgical recovery, our Physical Therapist will note your progress and be watchful for the development of fractures and instability. When your recovery is well under way, regular visits to FYZICAL Venice will end. Although we will continue to be a resource, you will eventually be in charge of doing some therapeutic exercises as part of an ongoing home program.
FYZICAL Venice provides services for Physical Therapy in Venice.