Neurological Physical Therapy
Neurological and Movement Disorders
At FYZICAL Lake Success, we offer highly effective physical therapy care, treating patients suffering from a wide variety of neurological and movement disorders. The following is a list of diseases and disorders affecting the neurological system that are managed at FYZICAL Lake Success.
- Bell's Palsy
- Brachial Plexus Injuries
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
- Concussions
- Diabetic Neuropathy
- Foot Drop
- Meralgia Paraesthetica
- Morton's Neuroma
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Parkinson's Disease
- Peripheral Neuropathy
- Strokes
- Thoracic Outlet
Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease is a progressive disorder of the nervous system that affects your movement. It develops gradually, sometimes starting with a barely noticeable tremor in just one hand. But while tremor may be the most well-known sign of Parkinson's disease, the disorder also commonly causes stiffness or slowing of movement.
In early stages of Parkinson's disease, your face may show little or no expression, or your arms may not swing when you walk. Your speech may become soft or slurred. Parkinson's disease symptoms worsen as your condition progresses over time. The movement centers of your nervous system become impaired, affecting your gait, balance and general mobility. Physical therapy has long been a key aspect of management of person's with Parkinson's; postural stability gait re-training and functional mobility are all addressed by the physical therapist.

Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a potentially debilitating disease in which your body's immune system damages the protective myelin sheath that covers your nerves. Damage to myelin causes interference in the communication between your brain, spinal cord and other areas of your body. This condition may result in deterioration of the nerves themselves, a process that's not reversible.
Symptoms vary widely, depending on the amount of damage and the nerves that are affected. Depending on where the nerve damage occurs, MS can affect vision, sensation, coordination, movement, and bladder and bowel control.. People with severe cases of multiple sclerosis may have postural [standing] instability and progressively lose the ability to walk or even speak clearly. Multiple sclerosis can be difficult to diagnose early in the course of the disease because symptoms often come and go - sometimes disappearing for months.
Multiple sclerosis has no cure. However, treatments may help treat MS attacks, manage symptoms and reduce progress of the disease. Physical therapy is important to maintain joint range of motion, preserve functional muscle strength, balance, gait and mobility.
Strokes
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of your brain is interrupted or severely reduced, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and food. Within minutes, brain cells begin to die. A stroke is a medical emergency and prompt treatment is crucial to control damage to the brain cells. Early action can minimize brain damage and potential complications.
The good news is that strokes can be treated and prevented, and many fewer Americans die of stroke now than even 15 years ago. Better control of major stroke risk factors - high blood pressure, smoking and high cholesterol - may be responsible for the decline. The physical impairments possible from stroke can create a variety of strength and movement dysfunction, limiting one's ability to sit, stand, walk and get around safely, with or without an assistive device. Physical therapists are well trained in the management of the various physical impairments suffered by those persons affected by the impact stroke.
Concussions
A concussion is a traumatic brain injury from a direct blow that alters the way your brain functions. Effects are usually temporary, but can include problems with headache, concentration, memory, judgment, balance and coordination.
Although concussions usually are caused by a blow to the head, they can also occur when the head and upper body are violently shaken as in an accident of some sports. These injuries can cause a loss of consciousness, but most concussions do not. Because of this, some people have concussions and don't realize it.
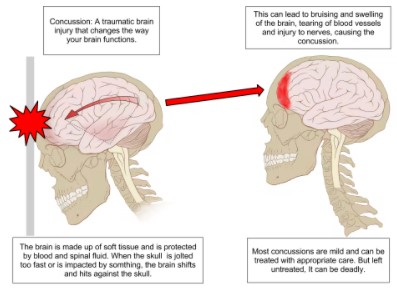
Concussions are common, particularly if you play a contact sport, such as football. But every concussion injures your brain to some extent. This injury needs time and rest to heal properly. Luckily, most concussive traumatic brain injuries are mild, and people usually recover fully. A medical evaluation is necessary to evaluate the severity of any concussion, in order to determine if treatment is indicated and also to determine when resumption of driving, work or sports is appropriate.
Post-concussion syndrome is a complex disorder in which a variable combination of post-concussion symptoms - such as headaches, dizziness and loss od balance - last for weeks and sometimes months after the injury that caused the concussion.
Concussion is a mild traumatic brain injury, usually occurring after a blow to the head. Loss of consciousness isn't required for a diagnosis of concussion or post-concussion syndrome. In fact, the risk of post-concussion syndrome doesn't appear to be associated with the severity of theinitial injury.
In most people, post-concussion syndrome symptoms occur within the first seven to 10 days and go away within three months, though they can persist for a year or more. Post-concussion syndrome treatments are aimed at easing specific symptoms. Physical therapists are often called upon to manage post traumatic position al vertigo and the loss of balance and equilibrium that often results in post-concussion syndrome. Computerized balance testing is very helpful in assessing patient condition, guiding treatment and determining progress objectively. Many athletic programs perform pre participation balance evaluation and screening in order to obtain an object baseline of the athlete's balance capabilities, in the event that a concussive injury is sustained during play.
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, a result of nerve damage, often causes weakness, numbness and pain, usually in your hands and feet, but it may also occur in other areas of your body. People generally describe the pain of peripheral neuropathy as tingling or burning, while they may compare the loss of sensation to the feeling of wearing a thin stocking or glove.
Peripheral neuropathy can result from problems such as traumatic injuries, infections, metabolic problems and exposure to toxins. One of the most common causes is diabetes.
In many cases, peripheral neuropathy symptoms improve with time, especially if the condition is caused by an underlying condition that can be treated nd resolved. Other types tend to be more chronic, such as diabetic neuropathy or chemotherapy related neuropathy. Both can impair your balance, gait and walking safety; problems that should be managed by your physical therapist.
Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that can occur if you have diabetes. High blood sugar can injure nerve fibers throughout your body, but diabetic neuropathy most often damages nerves in your legs and feet.
Depending on the affected nerves, symptoms of diabetic neuropathy can range from pain and numbness in your extremities to problems with your digestive system, urinary tract, blood vessels and heart. For some people, these symptoms are mild; for others, diabetic neuropathy can be painful, disabling and even fatal.
Diabetic neuropathy is a common serious complication of diabetes. Yet you can often prevent diabetic neuropathy or slow its progress with tight blood sugar control and a healthy lifestyle.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a progressively painful hand and arm condition caused by a pinched nerve in your wrist. A number of factors can contribute to carpal tunnel syndrome, including the anatomy of your wrist, certain underlying health problems and possibly patterns of hand use.
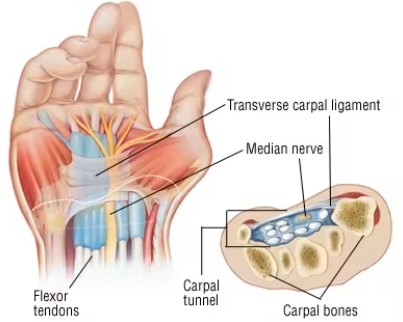
Bound by bones and ligaments, the carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway - about as big around as your thumb - located on the palm side of your wrist. This tunnel protects a main nerve to your hand and nine tendons that bend your fingers. Compression of the nerve produces the numbness, pain and, eventually, hand weakness that characterize carpal tunnel syndrome.
Fortunately, for most people who develop carpal tunnel syndrome, proper rest, work modification and physical therapy treatment usually can relieve the pain and numbness and restore normal use of their wrists and hands.
Foot Drop
Foot drop, sometimes called drop foot, is a general term for difficulty lifting the front part of the foot. If you have foot drop, you may drag the front of your foot on the ground when you walk. Foot drop isn't a disease. Rather, foot drop is a sign of an underlying neurological, muscular or anatomical problem. Foot drop often results from severe or unattended lumbar disc herniation, stroke or other localized nerve trauma in the lower leg. Sometimes foot drop is temporary. In other cases, foot drop is permanent. If you have foot drop, you may need to wear a brace on your ankle and foot to hold your foot in a normal position.
Bell's Palsy
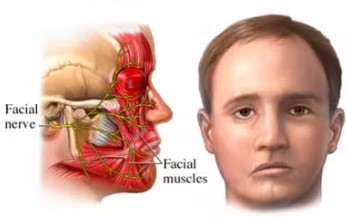
Bell's palsy causes sudden weakness in your facial muscles. This makes half of your face appear to droop. Your smile is one-sided, and your eye on that side resists closing. Bell's palsy, also known as facial palsy, can occur at any age. The exact cause is unknown, but it's believed to be the result of swelling and inflammation of the nerve that controls the muscles on one side of your face, possibly a reaction that occurs after a viral infection.
For some people, Bell's palsy is temporary, but medical evaluation and treatment should be immediate after onset. Symptoms may start to improve within a few weeks, with complete recovery in about six months. A small number of people continue to have some Bell's palsy symptoms for life. Rarely, Bell's palsy can recur. PT treatment is important to continue facial nerve impulses to the affected muscles, through electrical stimulation and exercise management to preserve remaining muscle function and promote facial muscle strengthening during the healing process.
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) is an uncommon form of chronic pain that usually affects an arm or leg. Complex regional pain syndrome typically develops after an injury, surgery, stroke or heart attack, but the pain is out of proportion to the severity of the initial injury, if any.
Previously called Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy (RSD) the cause of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome isn't clearly understood. Medical and physical therapy treatment [consisting of pain management and functional recovery techniques] for complex regional pain syndrome is most effective when started early. In such cases, improvement and even remission are possible.
Brachial Plexus Injuries
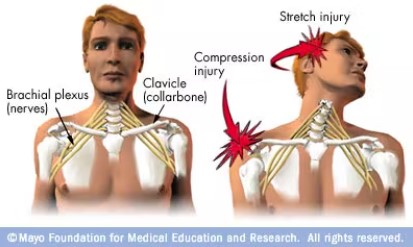
A brachial plexus injury is an injury to the brachial plexus - the network of nerves that sends signals from your cervical spine to your shoulder, arm and hand. A brachial plexus injury occurs when these nerves are stretched or, in the most serious cases, torn. This happens as result of your shoulder being pressed down forcefully while your head is pushed up and away from that shoulder.
Brachial plexus injuries are common in contact sports, but they frequently result from auto or motorcycle accidents or falls. Babies sometimes sustain brachial plexus injuries during birth. Other conditions, such as inflammation or tumors, may affect the brachial plexus. Minor injuries may respond well to time and conservative treatment with physical therapy [pain management and focused corrective muscle strengthening], but severe brachial plexus injuries may require surgical repair.
One type of brachial plexus injury is called a "stinger" or "burner." Stingers occur with compression or overstretching of the nerves that run from the neck to the arm, usually during collisions in contact sports.
Thoracic Outlet
The thoracic outlet is the space between your collarbone (clavicle) and your first rib. This narrow passageway is crowded with blood vessels, nerves and muscles.
Thoracic outlet syndrome is a group of disorders that occur when the blood vessels or nerves in the space between your collarbone and your first rib (thoracic outlet) become compressed. This can cause pain in your shoulders and neck and numbness in your fingers.
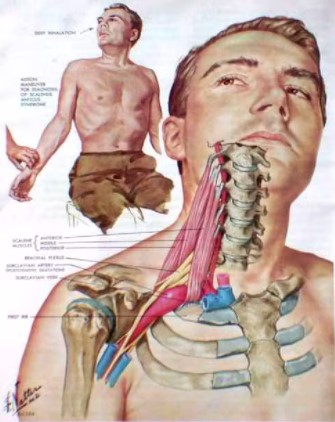
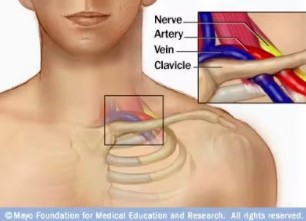
Common causes of thoracic outlet syndrome include physical trauma from a car accident, repetitive injuries from job- or sports-related activities, certain anatomical defects (such as having an extra rib), and pregnancy. Sometimes the cause of thoracic outlet syndrome is difficult or impossible to determine. Treatment for thoracic outlet syndrome usually involves physical therapy and pain relief measures. Most people improve with these approaches. In some cases, however, your doctor may recommend surgery in persistent and intractable cases.
Meralgia Paraesthetica
Meralgia paresthetica is a condition characterized by tingling, numbness and burning pain in the outer part of your thigh. The cause of meralgia paresthetica is compression of the [femoral] nerve that supplies sensation to the skin surface of your thigh. Tight clothing, obesity or weight gain, and pregnancy are common causes of meralgia paresthetica. However, meralgia paresthetica can also be due to local trauma or a disease, such as diabetes. In most cases, meralgia paresthetica can be relieved with conservative measures, such as wearing looser clothing. In more severe cases, treatment may include medications and/or physical therapy to relieve discomfort or, rarely, surgery.
Morton's Neuroma
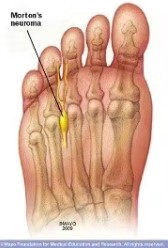
Morton's neuroma is a painful condition that affects the ball of your foot, most commonly the area between your third and fourth toes. Morton's neuroma may feel as if you are standing on a pebble in your shoe or on a fold in your sock.
Morton's neuroma involves a thickening of the tissue around one of the nerves leading to your toes. This can cause a sharp, burning pain in the ball of your foot. Your toes also may sting, burn or feel numb.
High-heeled shoes have been linked to the development of Morton's neuroma. Many people experience relief by switching to lower heeled shoes with wider toe boxes. Sometimes corticosteroid injections or surgery may be necessary.
Morton's neuroma involves a thickening of the tissue around one of the nerves leading to your toes. This can cause a sharp, burning pain in the ball of your foot. Your toes also may sting, burn or feel numb.
